Tokyo College Event“Facing the Challenges of Global Environmental Problems” by Dr. Yuan Tseh Lee

On November 27, 2019, Professor Yuan Tseh Lee (President Emeritus, Academia Sinica, Taiwan; former President of ICSU; Nobel Laureate in Chemistry, 1986) gave a lecture titled “Facing the Challenges of Global Environmental Problems.”
The emergence and development of human society
Professor Hisashi Nakamura (Research Center for Advanced Science and Technology, the University of Tokyo (RCAST)) moderated the event. Following opening remarks from Professor Ryohei Kanzaki, Director of RCAST, Professor Lee argued that the sun is extremely important for the development of both the earth and the humans and the other creatures that inhabit it. It is as a result of climatic stability that humans discovered agriculture. The creation of human society went hand-in-hand with the development of agriculture, but the Industrial Revolution led to people using fossil fuels such as oil more than solar energy. Human society, having seemingly severed its connection to the sun, has increased its consumption, putting a heavy burden on the planet. Ozone depletion began in the 1970s, and the human impact on the earth is now clearly visible in air pollution. Professor Lee stressed that it is not enough simply to think about avoiding burning coal as a regional issue, and that we need to focus on carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases as an international issue.
Facing the challenges of global environmental problems
Professor Lee warned that after the Industrial Revolution the connection between the earth and humankind was severed, as were the connections between people. He stated that, from a sustainable development perspective, we must reduce energy consumption, and seriously investigate how to shift towards solar and wind energy. However, it is not possible to use solar power everywhere on the planet. Cross-border ties are necessary to avoid disparities emerging in profitability according to population density when selling solar energy on the international market. Thus, Professor Lee argued that connections in human society have a bearing on the distribution of energy and benefits.
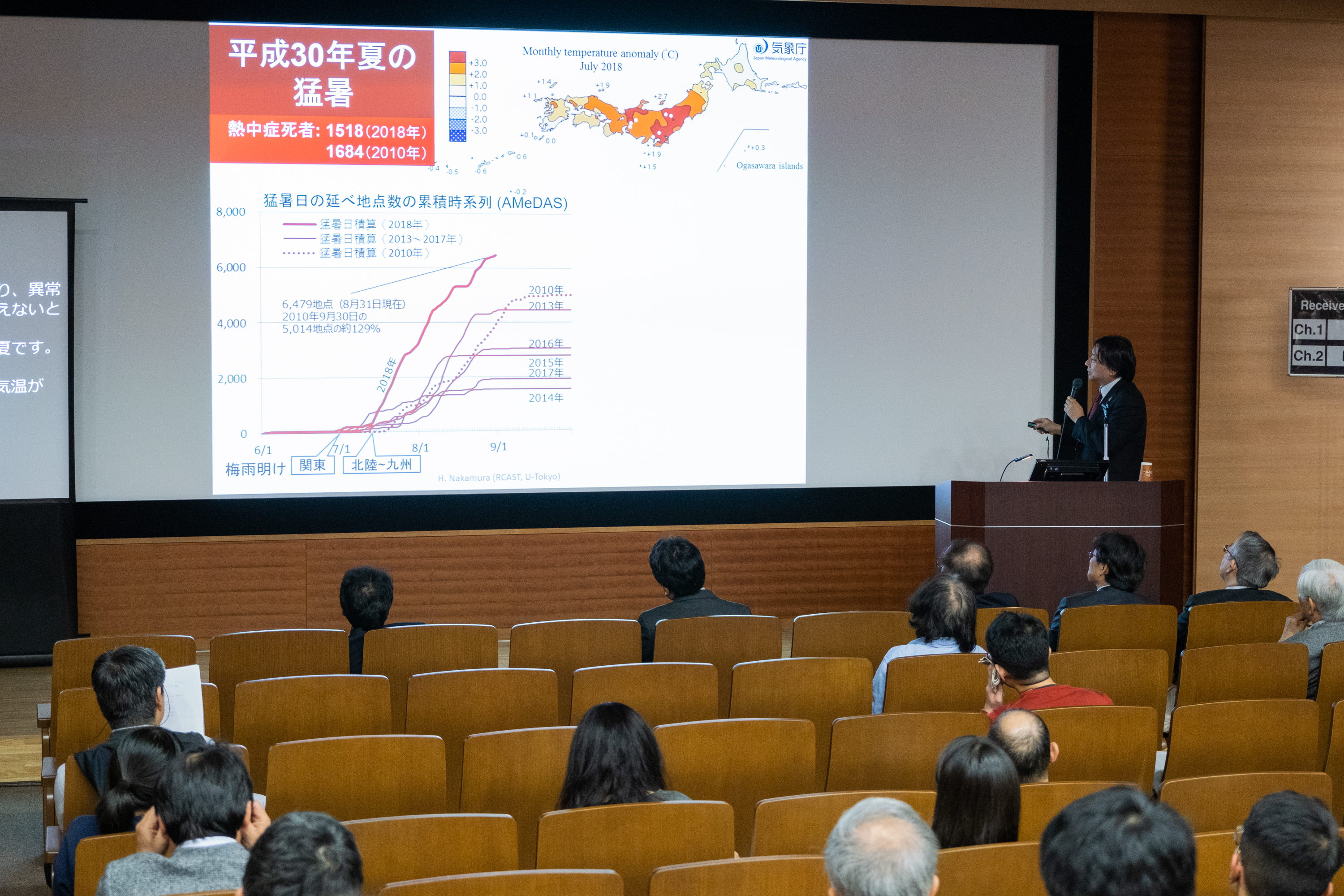
Following the lecture were comments from members of RCAST. Professor Takashi Kondo, a specialist in high performance materials, introduced the performance and characteristics of perovskite solar cells. Professor Masakazu Sugiyama, who specializes in energy systems, stated that systems should be changed together with devices. He said that we should consider systems that rely on hydrogen, together with hydrogen production powered by solar cells and wind turbines. Professor Hisashi Nakamura, a climate science specialist, talked about global warming and abnormal weather (changes to summer temperatures and humidity, strong rain, and ocean warming).
Q&A
In the Q&A session, there were questions from the floor in a range of areas, including how to effectively handle the carbon dioxide that we have created, the relationship between carbon dioxide density and global warming, and what the most important actions are, including for the general public. The speakers discussed the importance not only of developing new forms of energy, but also of everyone reducing their energy consumption, and ultimately pointed out the importance of international cooperation.
| Date(s) | Wednesday, 27 November 2019, 5:00-6:30 pm (Doors open: 4:30 pm) |
|---|---|
| Venue |
ENEOS Hall, The University of Tokyo (1F, RCAST Bldg. 3-South, Komaba II Campus) |
| Registration | Pre-registration required (150 seats - First come, first served) |
| Language | Japanese (English-Japanese simultaneous translation available) |
| Abstract |
Humans have changed the atmosphere through excessive use of energy from fossil fuels to the extent that the young will inherit an out-of-control environment. Scientists are working to create ways for a global economy with zero greenhouse gas emission by 2050. Problem though is not in the science and technology, but in the lack of political will and financial commitment to achieve that goal. This lecture aims to offer some ideas how to create the world we want by working together. |
| Organized by | Research Center for Advanced Science and Technology, The University of Tokyo Tokyo College, The University of Tokyo |
| Contact | tcevent@graffiti97.co.jp |